The knee joint is formed by the movable "tandem" of the tibia and femur.Prevents their lateral displacement, the patella and easy, sliding movement is provided by an elastic layer of continuous cartilage tissue.
The thickness of "healthy" cartilage, the articular surfaces of the extension of the bones of the knee joint is 5-6 mm.
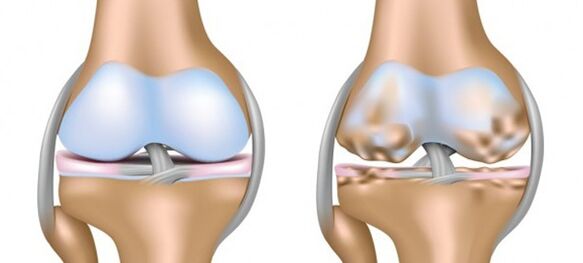
This is enough to soften the mechanical friction of the bones and absorb the "shock" load.A disease that causes the destruction of the natural shock absorption tissue and the destruction of joint deformation - gonarthrosis or arthrosis of the knee joint, unpleasant symptoms and treatment are often difficult with the use of a compensatory mechanism from the bone structures.
What causes the disease?
There is an opinion that gonarthrosis of the knee is the result of "salt deposition".However, calcium salts or deposition of calcium salts in the ligamentous apparatus of the knee has no independent significance and does not result in more than one reason.
What is gonarthrosis and how can it be treated?
In fact, the "starting point" should be considered a violation of small bone vessels and its consequence - difficulties in the cupping and depletion of cartilage tissue.This is followed by deformation of the hyaline cartilage.The latter abrasives are coated with versatile cracks.Synovial fluid becomes more viscous and loses its properties as a natural "moisturizer" of cartilage tissue.
The complete disappearance of drying "shock absorption" can be called the end of the pathological process.
However, the bones under the carina, which "lose their coverings", are covered with growths and "climbs" along the periphery and are covered with bone growths.In this case, the knee joint is deformed and the legs take an x- or o-shape, so this pathology is also called deformed osteoarthritis (hereinafter referred to as DOA).
What are the causes of arthrosis of the knee joint?
- Aging of the body and "wear and tear" of the joints;
- Excess body weight;
- Excessive loads in the middle of the knee (in athletes);
- Knee injury, fracture of one of the bones;
- Meniscus removal;
- Untreated arthritis, rheumatism;
- Abnormal location of the bony components of the joint;
- Hormones in the endocrine system and signaling, metabolic decmence.
Arthrosis is often confused with different types of arthritis.
However, the difference between arthritis and arthrosis of the knee joint is the result of invasion of the body by various pathogenic agents, which often "result" in inflammatory diseases of the whole body.
Sometimes, the symptoms of arthritis - swelling of the joint, swelling, swelling, pain that worsens at night - are the result of the immune system "putting" an active defense against the body's own cells.
Arthritis, which is only a local disease, is often the logical continuation of arthritis or the result of gradual "wear and tear" of the joint.
Primary and secondary gonarthrosis
In orthopedics and traumatology, the types of arthrosis of the knee joint generally differ depending on the causes that cause degenerative changes in the articular cartilage.
- Age-related or primary gonarthrosisThe knee joint often undergoes a relatively painless course of aging due to physical "wear and tear" of the cartilage tissue.A little more than men, women over the age of 40 face this form of the disease.Previously, the development of primary gonarthrosis threatens athletes and those with extra pounds;
- Secondary gonarthrosis- It develops at any age as a consequence of untimely treatment of previous injuries or inflammatory diseases.

Where is the disease?
It develops gradually, gonarthrosis is localized in the inner part of the knee joint.But the disease can "lurk" between the patella and the surface of the femur.
- Left-sided gonarthrosis often affects athletes and overweight people;
- Professional or sports activities involving excessive dynamic or static loads on the right leg are more sensitive to degenerative changes in the cartilage layer of the right knee joint;
- Bilateral gonarthrosis is often related to age.Regardless of the causes, in most cases uncontrolled destruction of both knee joints leads to disability.
Aw, it hurts!
Symptoms of gonarthrosis of the knee joint are quite vague at the beginning of the disease, and if they feel pain in the knee after a long hike, many people will not rush to visit a rheumatologist or an arthrologist.
After all, a short rest and relaxation relieves unpleasant symptoms in a slightly "crunchy" knee, gives a dubious feeling of physical well-being.
In fact, the "vague" symptoms of the first stages of degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system make it extremely difficult to detect and treat them in time.Deforming gonarthrosis is no exception.
- Stage 1 Gonarthrosis, mild discomfort caused only by fatigue of the limb, it is quite difficult to recognize yourself.A timely impetus to visit a doctor is often given by a dull pain in the knee and a "crushing" of rough cartilage intermingled;
- 2nd degree gonarthrosis sets the stage for the deformation of the knee joint and hinders its movements in the morning, causing "separation".Strong, prolonged pain occurs after standing for a long time or sitting for a long time.Moderately limited mobility of the knee, accompanied by a stabbing sound;
- The maximum symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint appear in the third stage of the disease.A swollen knee, local temperature increases, often hurts to rest.
The movement of the joint is blocked by sharp pain caused by "Joint mouse" - fragments of broken bone growths.
A deformed joint loses stability and is difficult to move.An advanced disease at this stage requires a prosthesis.
Can knee osteoarthritis be treated?
The well-known phrase "Rest is not an end in itself, but a means to an end" is directly related to those who encounter the initial manifestations of the disease.The rest ensures the maximum release of the knee joint during another operation.The use of individual orthopedic traces is recommended for the same purpose.
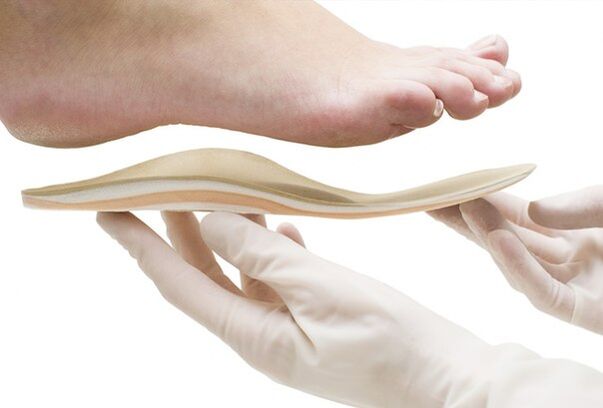
The use of individual orthopedic traces will provide maximum relief of the knee joint.
An insurance against disease, more precisely, in athletes, there will be special means that support the stability of the "loose" knee joint.
A cane will help elderly people "unload" their joints when walking.But the measures listed are more likely to prevent arthrosis of the knee joints.If such a "vaccination" did not help, and the worsening gonarthrosis manifests itself with inflammation and pain, you should hurry to see an orthopedist or arthrologist.
How to treat gonarthrosis?
- Stage 1.Inflammation and accompanying pain.Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs used orally, intramuscularly or intravenously will cope with the "acute" problem.In rectal suppositories, NSAIDs will have a "sealed" long-lasting effect.
The use of corticosteroids is also justified - they are "delivered" directly to the diseased joints.
Local use of ointments or gels with an active anti-inflammatory component will help increase the anti-inflammatory effect of internally used NSAIDs.The latter helps to quickly relieve swelling.

Drugs that reduce vascular muscle tone are often prescribed together with NSAIDs.This improves periphericular blood flow.
What to do with arthrosis of the knee joint, for example, for patients suffering from gastrointestinal diseases taking NSAIDS and pain relievers?
Oxygen therapy would be a good alternative.
- Stage 2."Nourish" dried cartilage with substances that stimulate collagen synthesis.Chondroprotectors intended for this purpose act slowly, but long-term use promotes the synthesis of natural components of the cartilage matrix.The greatest effect is achieved by the administration of narcotics.
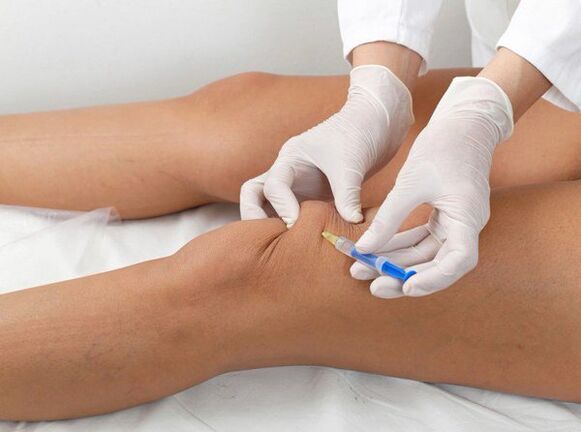
- Stage 3.We smooth cartilage "roughness" and reduce cartilage friction by introducing hyaluronic acid.
- Stage 4.Using physiotherapy, we improve joint blood supply and cubism of the joint.For this purpose, it is recommended to combine work with pleasure and undergo sanatorium-resort treatment.
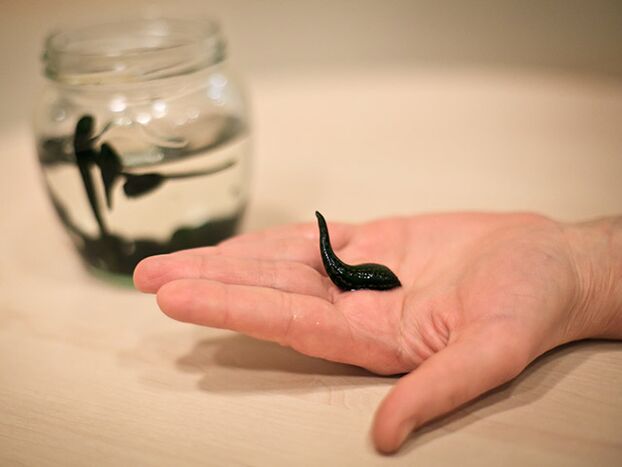
- Stage 5.We use non-traditional treatment methods: acupuncture and hirudotherapy, aparapia.An innovation in the treatment of Knee Joint Doa is a one-step drug administration, a serum ortfine obtained from the patient's blood proteins.

What are the right exercises?
Physical therapy will help slow down the progressive destruction of the articular elements.Its main goals:
- improving joint blood supply and activating the cup of all its components;
- increased knee mobility;
- Cultivating the tone of all the muscles of the human body.
Physical therapy sessions are recommended, at least initially, under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor.An experienced trainer will choose exercises that match the level of joint mobility, except for high-amplitude and exercises with excessive axial load - everything can damage the soft tissues of the joint and worsen the patient's condition.
Recipes from the green pharmacy: there are options!
Provides gonarthrosis and treatment by traditional methods:
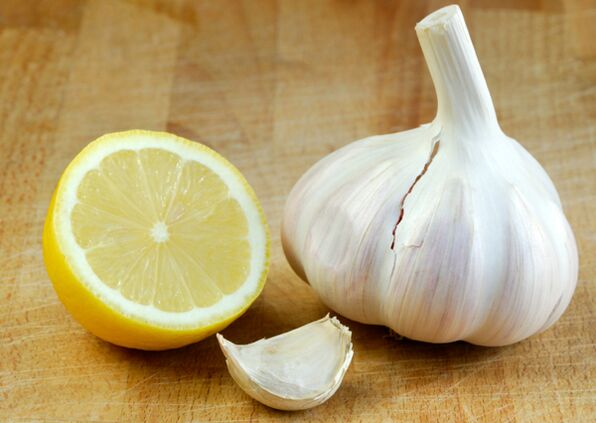
- Option 1.120 g thick garlic, 250 g celery root and 3 lemons in a meat grinder.Put the mixture in a 3-liter container and fill it with boiling water.After keeping it overnight in a warm place, wrap the well of the jar, start taking it in the morning, consume 70 grams of medicine every morning.Gradually increase the intake by 3 times;
- Option 2.Treat a painful joint with a mixture of 1 tbsp.l.honey and 3 tbsp.l.Apple Cider Vinegar.Put a fresh cabbage leaf on top (lightly beat with a knife) or burdock (light side on the joint).Wrap your foot in cellophane film and a soft scarf.Do up to 30 procedures a night.

An inevitable decision
Often severe pain and joint dysfunction threaten disability.
Then middle-aged patients, as well as young people diagnosed with arthrosis of the knee joint, require surgery.
The most common procedure is endoprosthetics.The duration of such an operation is no more than an hour, and its effect is the pain-free functioning of the "restored" extremity for at least 20 years.Over time, the "loose" prosthesis must be replaced.
























